| Fort Name : | Alphabetically | RangeWise | DistrictWise | CategoryWise | GradeWise |
| Chavand | FortHeight : 3400 ft. | ||||
| Type : Hill forts | Fort Range : Naneghat | ||||
| District : Pune | Grade : Medium | ||||
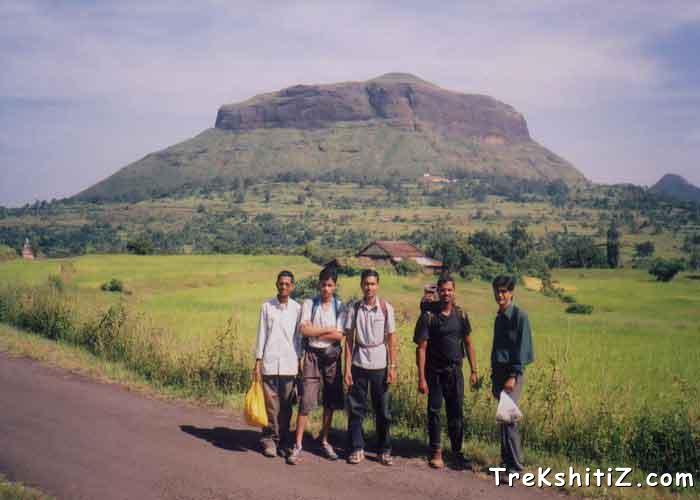
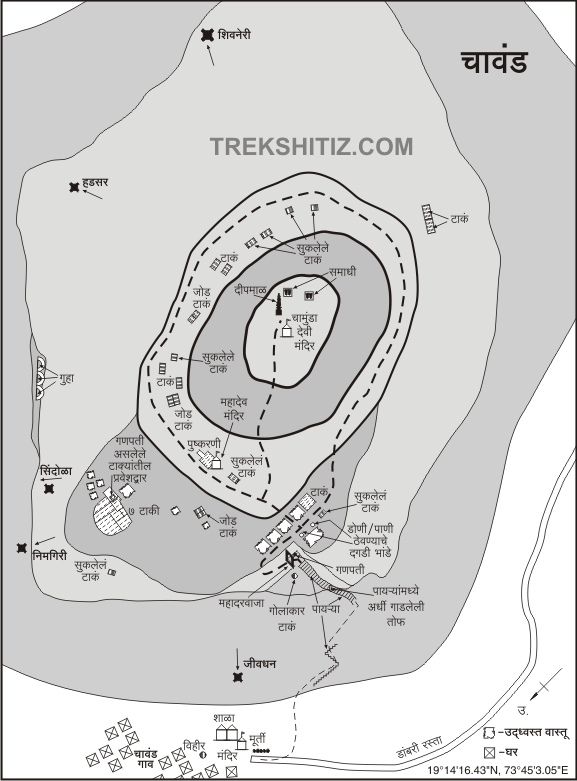
| Sahyadri is not just a mountain range, but it is a great treasure of history, the history of the struggle by the great Marathas, & ancient Satvaahans, who left for us with their fine arts with which very few modern carvings can be compared. The Satvaahans ruled what is today called the state of Maharashtra, & their great regime is commemorated by the remnants of the forts & caves they constructed in the heart of the Sahyadris. The whole range that has been guarding the ancient commercial route of Naneghat for thousands of years includes the forts of Jeevdhan, Hadsar, and Mahishgad & Chavand. These belong to the Satvaahan era. And Chavand being one of them is a very significant one. Situated at a height of 3000ft from sea level, the fort houses many a remnant of constructions that take us about 800 years back into the time. The fort is in Pune district, at a distance of 20 km from the city of Junnar. The region at the foothills of the fort contains exotic flora & fauna. It was here that we could spot at least 12 varieties of birds. Village of Chavandwadi lies at the base of the fort. |
|||||
|
|||||
| History : | |||||
| Medieval period Malik Ahmed founded the Nizam Dynasty in 1485. He was the first Nizamshah who acquired the fort of Chavand after the dissolution of the Bahmani Empire. The seventh Nizamshah was Second Burhanshah. His grandson Bahadurshah was imprisoned here in 1594. Bahadurshah was the nephew of Chandbibi, a renowned personality from the same period. She played an important role in helping him to achieve the throne. In 1636 Shahajiraje, father of Shivaji Maharaj, signed a treaty with the Moghals, in which the Moghals got Chavand. Shivaji Maharaj named the fort as “Prasannagad”. Mythological references 1) The forts named after the names of great sages (for e.g. Vasota, named after Vasistha) are pre-ancient forts. 2) The forts decorated by Buddhist carvings and sculptures (for e.g. Shivneri) are ancient forts. 3) Forts belonging to the medieval period are related to Shaiva, Shakta or Naath. 4) The goddess Chamunda is an idol of destruction of evil, with a terrifying appearance, armed with weapons. The deity belongs to Bengal, Bihar and Karnataka. |
|||||
| Fascinating Spots : | |||||
| 1. Saptamatrika (The seven cisterns) : | |
| The British in their attack have destroyed many a construction in the eighteenth century. Here a temple half buried in the earth can be seen. As we go ahead on the left, we can see 7 water tanks aligned along each other. These have much mythological significance, & their names are as follows: Brahmi, Maheshwari, Kaumari, Vaishnavi, Varahi, Indrayani & Chamunda, the most powerful goddess of all. | |
| 2. Human made caves : | |
| As we proceed towards the northern direction around the fortification, we can see that a proper way was constructed hereby to move around to keep watch. On the north side of the fort, human made caves are situated where the fortification ends. Here it is said that a secret passage exists, amidst the wall, right below the caves. As we go the south side, we can have a beautiful view of the river Kukdi that originates from Kukdeshwar, a famous pilgrimage near the fort. On the southeastern side, no fortification exists as steep fall dominates this place. Again as we proceed westwards, we can see the fortification here. This fort being strongly secured was used for imprisoning Bahadurshah Nizam in 1594. | |
| 3. Temple of goddess Chamunda : | |
| On the topmost part of the fort, i.e. on a small hillock, is situated the temple of Goddess Chamunda. Here rises the question, that who brought this deity here in Maharashtra, which is predominantly from the provinces of Bengal, Bihar & Mysore. The answer is also quite simple. Naneghat had been the main route for transport of goods that came from other provinces via harbour of Sopara & Kalyan, the place of junction. Some well established businessman from Mysore, who came through Naneghat, must have established Chamunda here. Folks were unable to utter Chamunda, & they called it as Chavand, hence was named the fort. The places in the region of Naneghat reflect the rich culture of Satvaahan dynasty, and the well-developed artistic works that existed during this era. The temple of “Kukdeshwar” must be visited when we go to Chavand. The simplicity of this place is worth experiencing. The caves of Shivneri and “Lenyadri”, another famous pilgrimage, are worth visiting. From the top of the fort, we can have a glimpse of the mountain of Shambhu & the fort of Jeevdhan on the west, Hadsar on the north, Shivneri on the east & the route of Naneghat along the fort. The topmost part of Shivneri is clearly visible from here. Along with a rich geographical position, the fort also has a rich history, which can be stated in a few steps. | |
| 1. Saptamatrika (The seven cisterns): : | |
| The British in their attack have destroyed many a construction in the eighteenth century. Here a temple half buried in the earth can be seen. As we go ahead on the left, we can see 7 water tanks aligned along each other. These have much mythological significance, & their names are as follows: Brahmi, Maheshwari, Kaumari, Vaishnavi, Varahi, Indrayani & Chamunda, the most powerful goddess of all. | |
| Ways To Reach : | |
| The way to the top of the fort goes along the village school, from the western side of the fort. From here, it takes about 45 minutes to reach the entrance door. From here the footsteps take us to the plains, on which we can see the remnants of many constructions. | |
| Accommodation Facility : | |
| One can stay on the fort in the caves, but mice may pose a problem. Trekkers also stay in the village school. There is boarding facility in Kukdeshwar temple too. | |
| Food Facility : | |
| Available in base village. | |
| Drinking Water Facility : | |
| There are many a cisterns and tanks on the fort, but the two on the southwest side are more reliable. | |
| Time To Reach : | |
| 45 minutes |
| Marathi Version |