| Gavilgad |
FortHeight : 3600 |
| Type : Hill forts |
Fort Range : Satpuda(Melghat) |
| District : Amravati |
Grade : Medium |
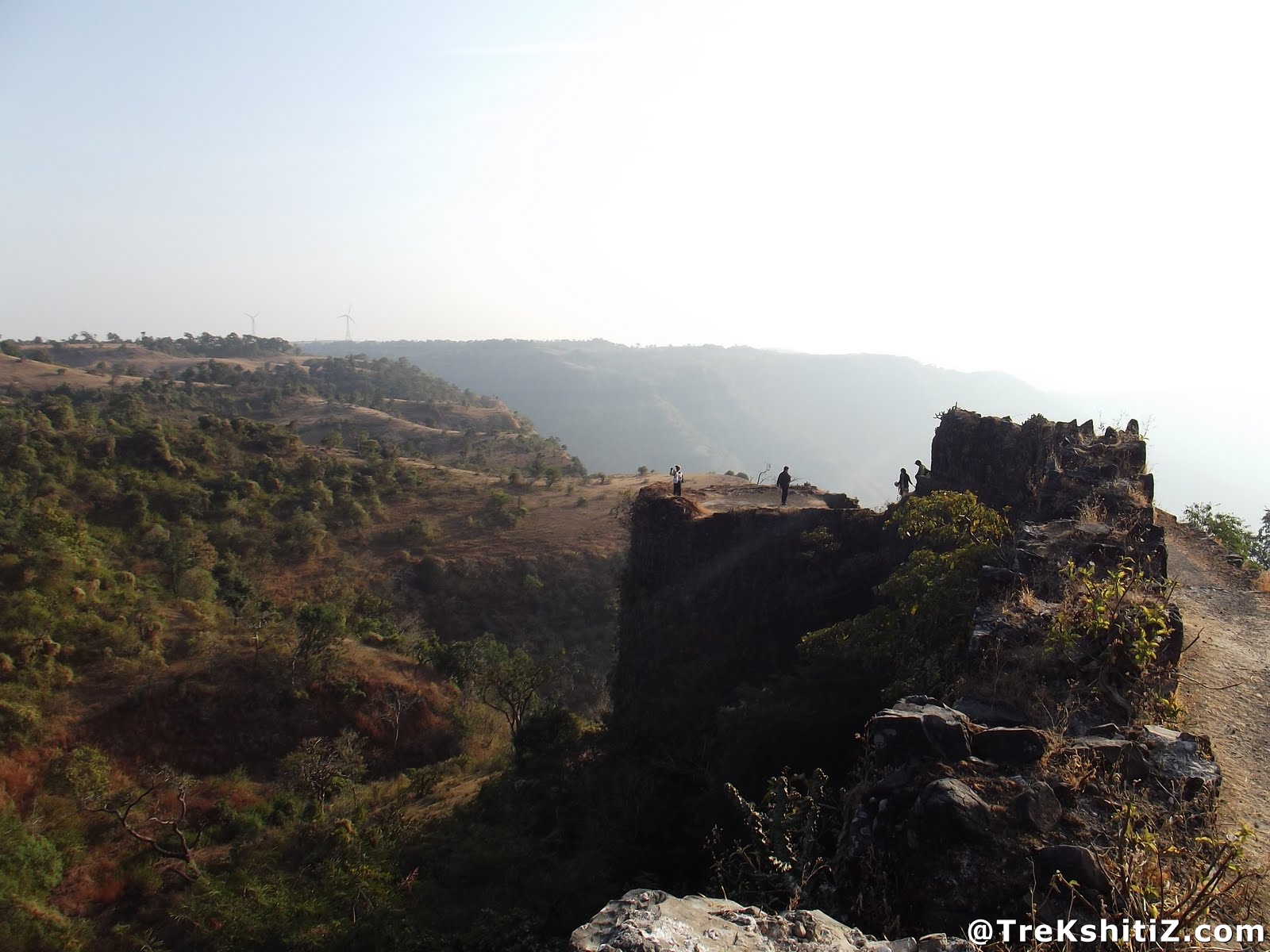
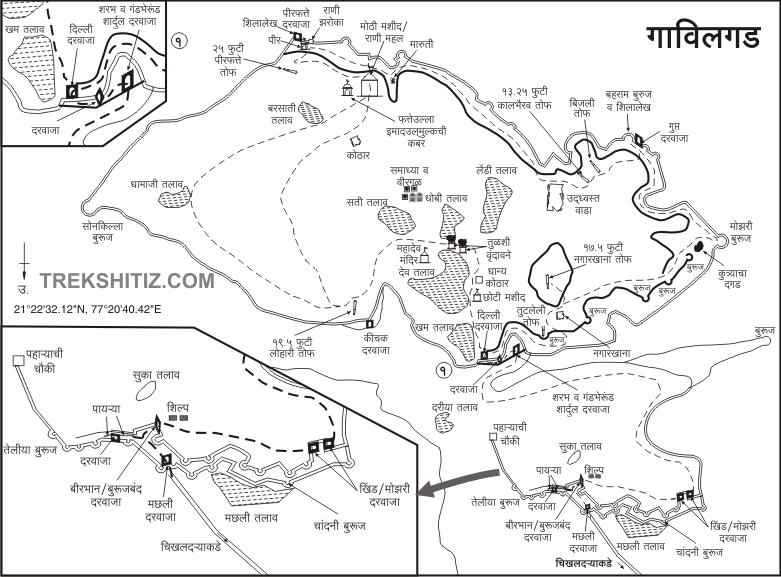
Gavilgad: the fort of Gavilgad took its name from the pastoral Gavlis centuries ago. They have deserted the fort. now. There are no inhabitants save the occasional visits of a panther or two and the herds of cattle who come to drink water from the tanks which once supplied water to a stately court and a strong garrison. Even to-day two tanks are in good condition but they are heavily silted and there is an abundance of shrub growth inside them which has rendered the waters putrid and useless for drinking. The tanks are known as Devatalav and Khantalav. In the monsoon the water overflows in a torrent down the precipitous hill side. The durbar steps on which princes had held audience are a favourite resort for picnic from Cikhaldara in the hot weather, the great banyan tree which has spread its boughs across them affording a delightful shade; while another class of sightseers has scribbled its names on the walls of the lesser mosque. The Archaeological department has concluded that it is impossible to do anything to restore the ruins; and though money is spent from time to time in removing rank vegetation from the walls, they are bound, as years pass by, to lapse into greater decay.
|
|
|
| History : |
The fort takes its name from the Gawli (cow herds) who inhabited the Berar (modern day Amravati) for centuries. Earlier the fort was likely just made of mud as were several such areas in the region. The exact date of construction is not known but the Persian historian, Firishta, records that Ahmed Shah Wali, the ninth king of the Muzaffarid dynasty built Gawilgarh when he was encamped at Ellichpur in 1425. Likely this was the date when major fortification was carried out.
In 1803 during the 2nd Maratha War the fort was besieged by Arthur Wellesley (later Duke of Wellington).[3] After two failed attempts at the main gate by British and Sepoy companies, and many casualties, Captain Campbell led the 94th Scottish Brigade (light company) up the ravine dividing the inner and outer forts and into the inner fort by escalade. The Scots then forced the northern gatehouse and opened the many gates, allowing the remaining British forces entry. The British suffered few casualties in the final assault (approx. 150). The fortress was returned to the Marathas after making peace with the British but they abandoned it. |
| Fascinating Spots : |